Setting up Merge Replication in SQL Server 2005SQL Server 2005 - Merge Replication Step by Step Procedure
Replication is a set of technologies for copying and distributing data and database objects from one database to another and then synchronizing between databases to maintain consistency. Using replication, you can distribute data to different locations and to remote or mobile users over local and wide area networks, dial-up connections, wireless connections, and the Internet.
Replication is the process of sharing data between databases in different locations. Using replication, we can create copies of a database and share the copy with different users so that they can make changes to their local copy of the database and later synchronize the changes to the source database.
Replication agents involved in merge replication are snapshot agent and merge agent.
Implement merge replication if changes are made constantly at the publisher and subscribing servers, and must bemerged in the end.
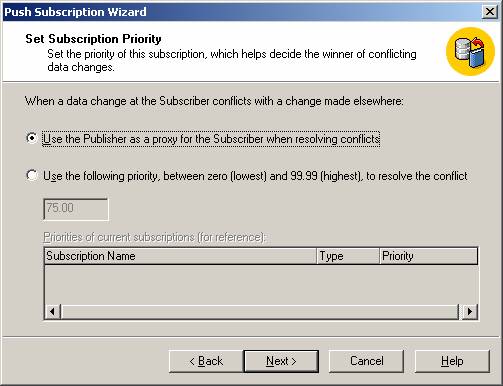
By default, the publisher wins all conflicts that it has with subscribers because it has the highest priority. The conflict resolver can be customized.
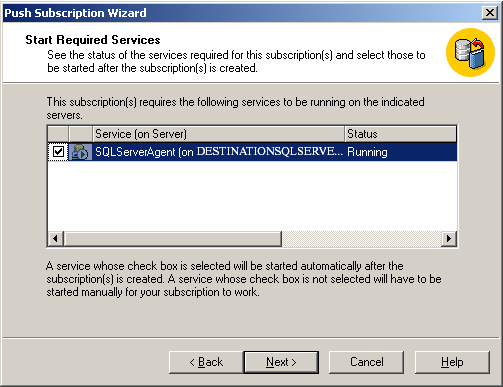
Note: Check that SQL Server Agent is running on the publisher and the subscriber.
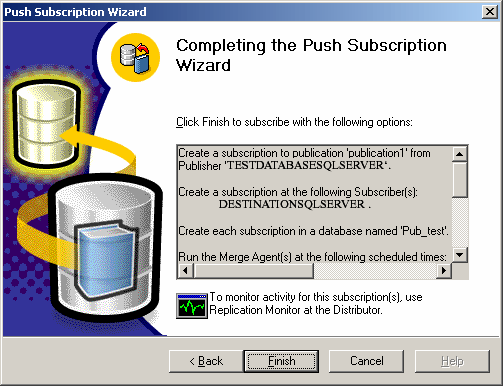
and then next up to the final step, and click Finish.
You can check errors from the "Replication Monitor" by right clicking on Local Replication --> Launch ReplicationMonitor.
Replication is the process of sharing data between databases in different locations. Using replication, we can create copies of a database and share the copy with different users so that they can make changes to their local copy of the database and later synchronize the changes to the source database.
Terminologies before getting started
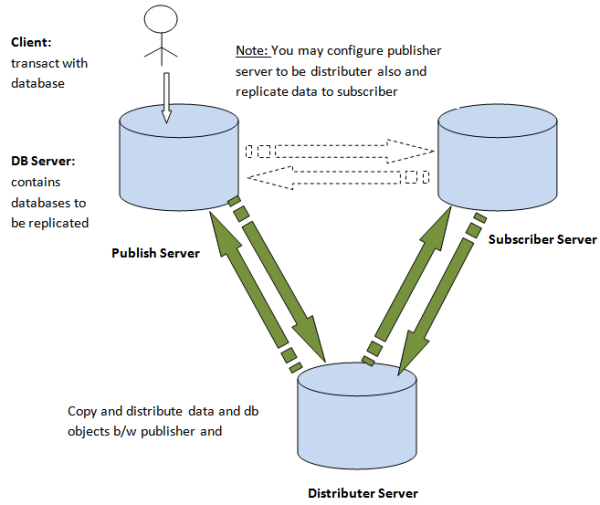
Microsoft SQL Server 2000 supports the following types of replication:- Publisher is a server that makes the data available for subscription to other servers. In addition to that, publisher also identifies what data has changed at the subscriber during the synchronizing process. The publisher contains publication(s).
- Subscriber is a server that receives and maintains the published data. Modifications to the data at the subscriber can be propagated back to the publisher.
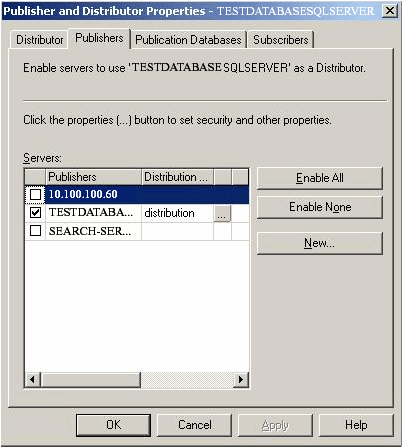
- Distributor is the server that manages the flow of data through the replication system. Two types of distributors are present, one is the remote distributor and the other the local distributor. The remote distributor is separate from the publisher and is configured as the distributor for replication. The local distributor is a server that is configured as the publisher and distributor.
- Agents are the processes that are responsible for copying and distributing data between the publisher and subscriber. There are different types of agents supporting different types of replication.
- Snapshot Agent is an executable file that prepares snapshot files containing schema and data of published tables and database objects, stores the files in the snapshot folder, and records synchronization jobs in the distribution database.
- An article can be any database object, like Tables (Column filtered or Row filtered), Views, Indexed Views, Stored Procedures, and User Defined Functions.
- Publication is a collection of articles.
- Subscription is a request for a copy of data or database objects to be replicated.

Replication types
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 supports the following types of replication:- Snapshot replication
- Transactional replication
- Merge replication
Snapshot replication
- Snapshot replication is also known as static replication. Snapshot replication copies and distributes data and database objects exactly as they appear at the current moment in time.
- Subscribers are updated with the complete modified data and not by individual transactions, and are not continuous in nature.
- This type is mostly used when the amount of data to be replicated is small and data/DB objects are static or does not change frequently.
Transactional replication
- Transactional replication is also known as dynamic replication. In transactional replication, modifications to the publication at the publisher are propagated to the subscriber incrementally.
- Publisher and the subscriber are always in synchronization and should always be connected.
- This type is mostly used when subscribers always need the latest data for processing.
Merge replication
It allows making autonomous changes to replicated data on the Publisher and on the Subscriber. With mergereplication, SQL Server captures all incremental data changes in the source and in the target databases, and reconciles conflicts according to rules you configure or using a custom resolver you create. Merge replication is best used when you want to support autonomous changes on the replicated data on the Publisher and on the Subscriber.Replication agents involved in merge replication are snapshot agent and merge agent.
Implement merge replication if changes are made constantly at the publisher and subscribing servers, and must bemerged in the end.
By default, the publisher wins all conflicts that it has with subscribers because it has the highest priority. The conflict resolver can be customized.
Before starting the replication process
Assume that we have two servers:- EGYPT-AEID: is the publisher server (contains HRatPublisher)
- SPS: is the subscriber server (contains HRatSubscriber) use SQL Server Authentication mode for login
Note: Check that SQL Server Agent is running on the publisher and the subscriber.
Steps
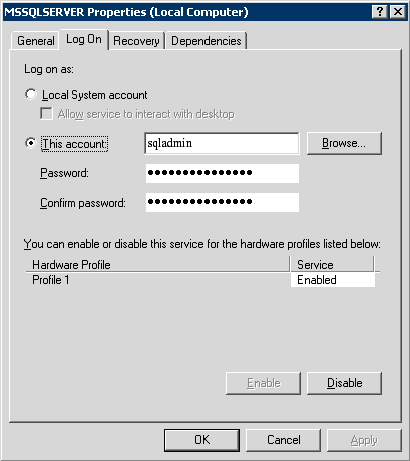
- Open SQL Server Management Studio and login with SQL Server Authentication to configure Publishing, Subscribers, and Distribution.
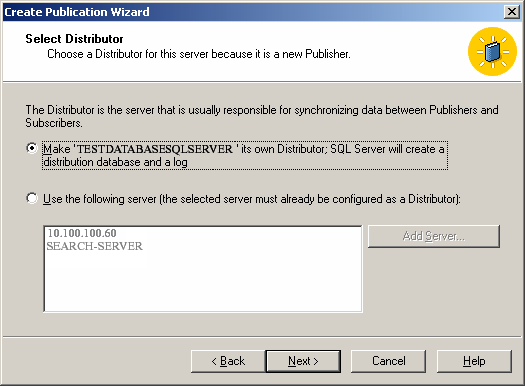
- Configure the appropriate server as the publisher or distributor.
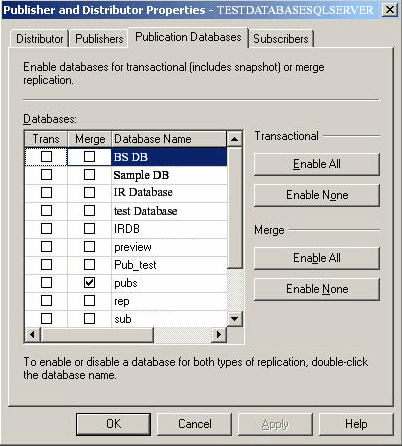
- Enable the appropriate database for merge replication.
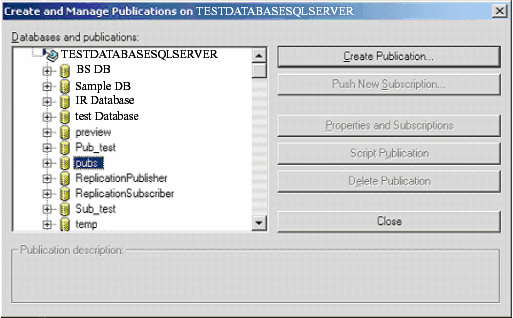
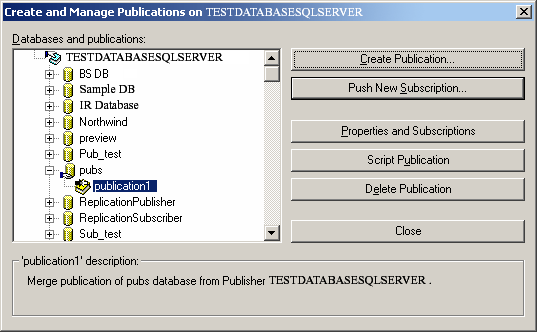
- Create a new local publication from DB-Server --> Replication --> Local Publications --> Right click --> New Pub.
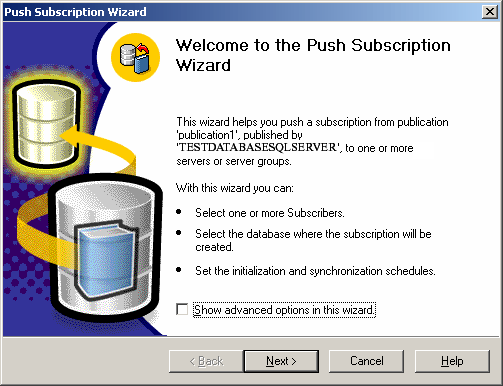
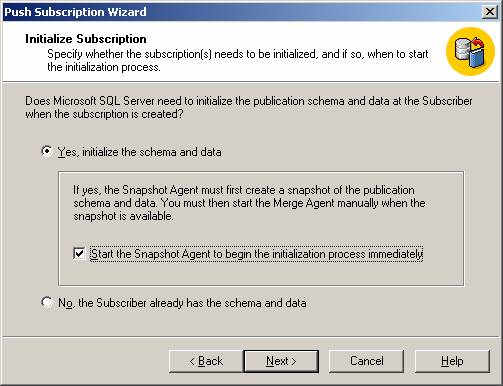
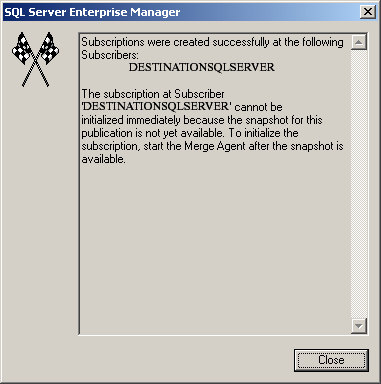
- Create a new subscription for the created "MyPublication01" publication by right clicking on MyPublication01 --> New Subscription. Configure the "Merge Agent" for the replication on the subscriber database.


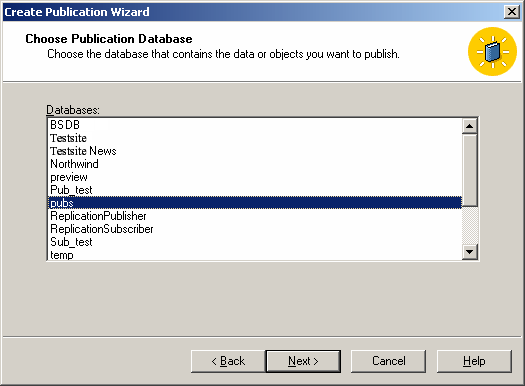
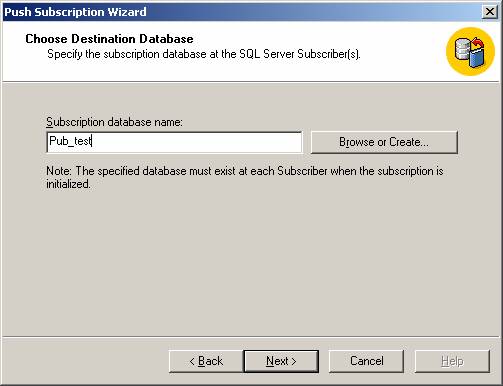
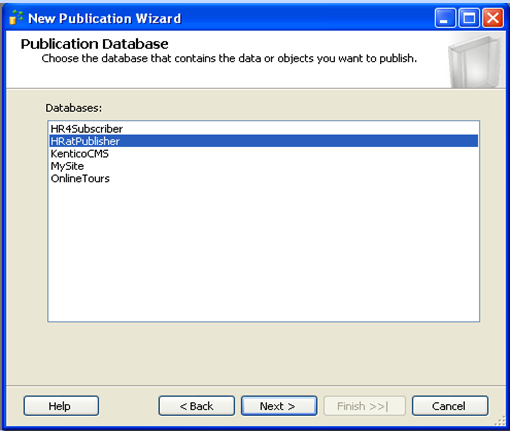
Then choose the database that contains the data or objects you want to replicate.
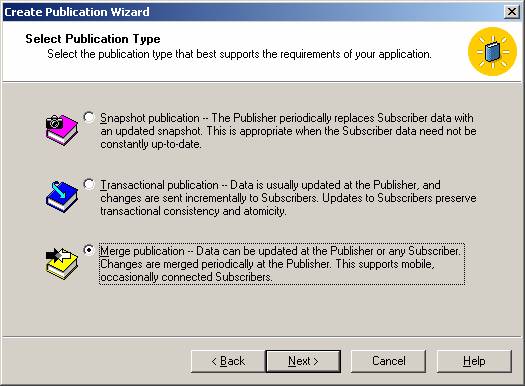
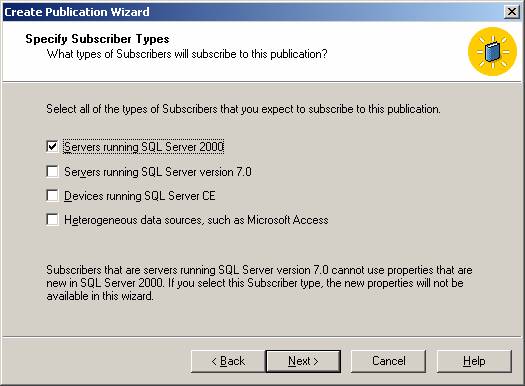
Choose the replication type and then specify the SQL Server versions that will be used by subscribers to that publication, like SQL Server 2005, SQL Mobile Edition, SQL for WinCE, etc.

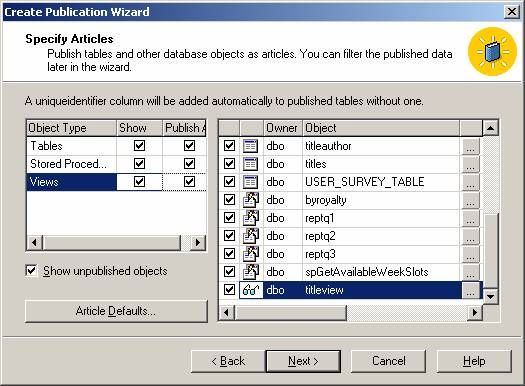
After that, manage the replication articles, data, and database objects by choosing the objects to be replicated.
Note: you can manage the replication properties for the selected objects.

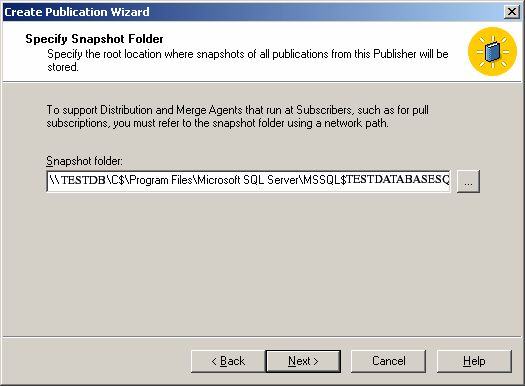
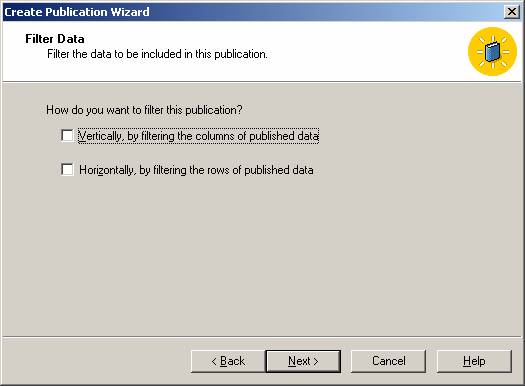
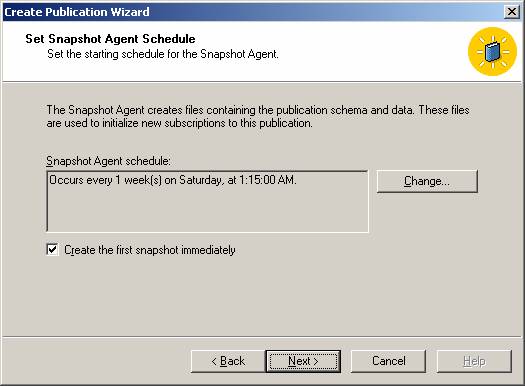
Then add filters to the published tables to optimize performance and then configure the snapshot agent.
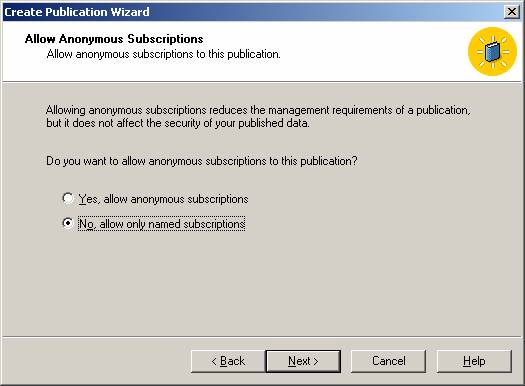
and configure the security for the snapshot agent.

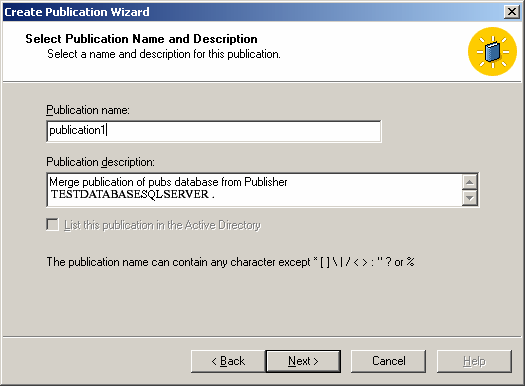
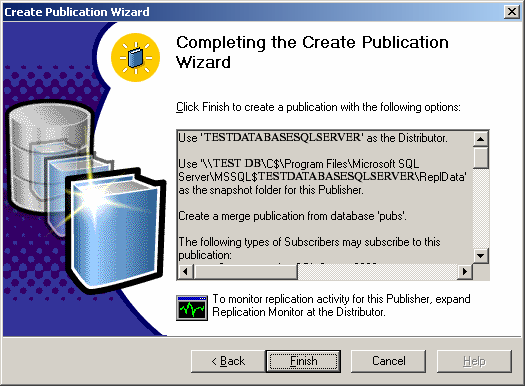
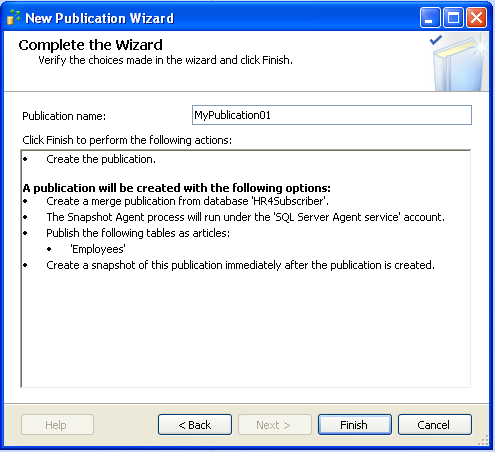
Finally, rename the publication and click Finish.


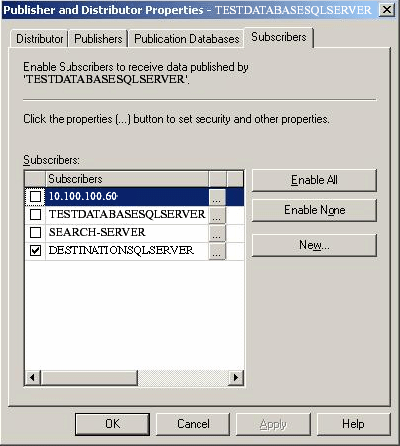
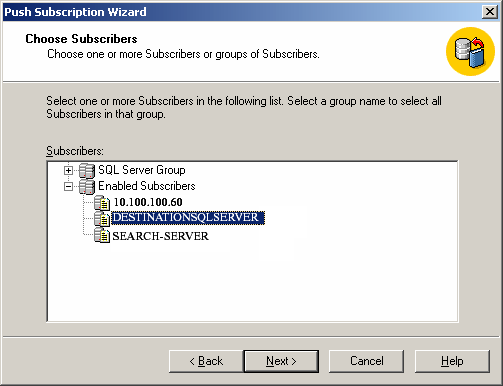
Choose one or more subscriber databases. You can add new SQL Server subscribers.
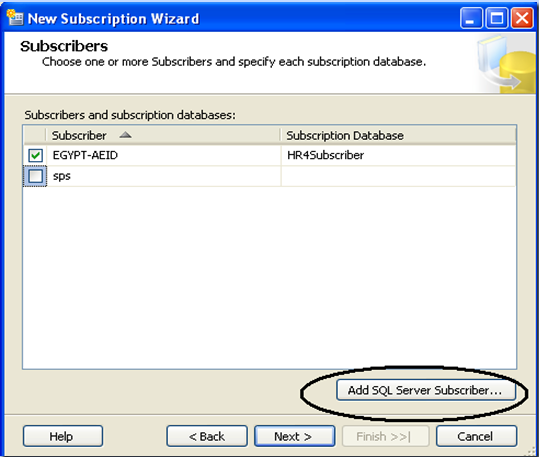
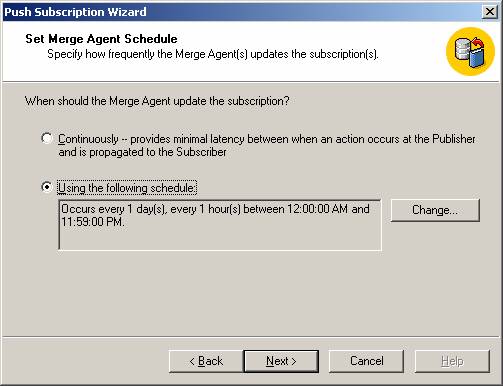
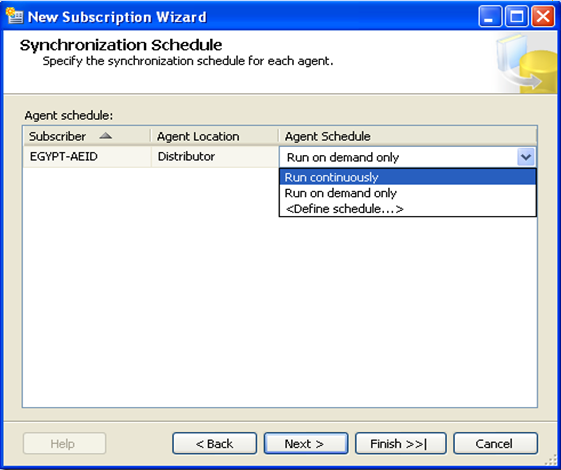
Then specify the Merge Agent security as mentioned above on "Agent Snapshot". And specify the synchronization schedule for each agent.
- Run continuously: add schedule times to be auto run continuously
- Run on demand only: manually run the synchronization

and then next up to the final step, and click Finish.
You can check errors from the "Replication Monitor" by right clicking on Local Replication --> Launch ReplicationMonitor.
Advantages of Replication
Users can avail the following advantages by using a replication process:- Users working in different geographic locations can work with their local copy of data, thus allowing greater autonomy.
- Database replication can also supplement your disaster-recovery plans by duplicating the data from a local database server to a remote database server. If the primary server fails, your applications can switch to the replicated copy of the data and continue operations.
- You can automatically back up a database by keeping a replica on a different computer. Unlike traditional backup methods that prevent users from getting access to a database during backup, replication allows you to continue making changes online.
- You can replicate a database on additional network servers and reassign users to balance the loads across those servers. You can also give users who need constant access to a database their own replica, thereby reducing the total network traffic.
- Database-replication logs the selected database transactions to a set of internal replication-management tables, which can then be synchronized to the source database. Database replication is different from filereplication, which essentially copies files.
Replication performance tuning tips
- By distributing partitions of data to different subscribers.
- When running SQL Server replication on a dedicated server, consider setting the minimum memory amount for SQL Server to use from the default value of 0 to a value closer to what SQL Server normally uses.
- Don’t publish more data than you need. Try to use row filter and column filter options wherever possible as explained above.
- Avoid creating triggers on tables that contain subscribed data.
- Applications that are updated frequently are not good candidates for database replication.
- For best performance, avoid replicating columns in your publications that include
TEXT,NTEXT, orIMAGEdata types.