Microsoft SQL Server: Get Current SQL Server Services using T-SQL(single Inst)
SQL Server service account information is stored in Windows Registry database. You can get this information from Services Console or SQL Server Configuration Manager.
To get account information from Services Console:
1. Go to Start > Run > Services.msc
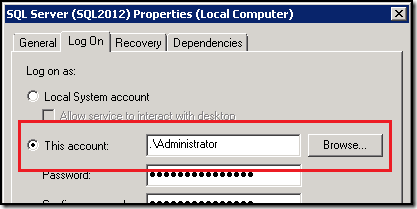
2. Right Click on SQL Server Service, i.e. “SQL Server (InstanceName)” and go to properties
3. The account information is available under Log On tab:
We can also get this information using T-SQL, we can use extended system stored procedurexp_instance_regread to read Windows Registry. Use below code to get information for SQL Server and SQL Server Agent Services:
DECLARE @DBEngineLogin VARCHAR(100)
DECLARE @AgentLogin VARCHAR(100)
EXECUTE master.dbo.xp_instance_regread
@rootkey = N’HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE’,
@key = N’SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSSQLServer’,
@value_name = N’ObjectName’,
@value = @DBEngineLogin OUTPUT
EXECUTE master.dbo.xp_instance_regread
@rootkey = N’HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE’,
@key = N’SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SQLServerAgent’,
@value_name = N’ObjectName’,
@value = @AgentLogin OUTPUT
SELECT [DBEngineLogin] = @DBEngineLogin, [AgentLogin] = @AgentLogin
GO
Result Set:
DBEngineLogin AgentLogin
.\Administrator NT AUTHORITY\NETWORKSERVICE
(1 row(s) affected)
We can use same registry for default and named instances as xp_instance_regread returns instance specific registry.
With SQL Server 2008 R2 SP1 and above a new server related DMV sys.dm_server_servicesis available which returns information of all instance services. This view also returns additional information about each of services such as startup type, status, current process id, physical executable name. We can also query service account name using this DMV:
SELECT servicename, service_account
FROM sys.dm_server_services
GO
Result Set:
servicename service_account
SQL Server (SQL2012) .\Administrator
SQL Server Agent (SQL2012) NT AUTHORITY\NETWORKSERVICE
SQL Full-text Filter Daemon Launcher (SQL2012) NT AUTHORITY\LOCALSERVICE
(3 row(s) affected)